Modern lifestyles often involve prolonged sitting at work, during commutes, or while watching TV. However, excessive sitting has been linked to numerous health risks, making it a significant public health concern. Understanding these dangers and taking proactive steps can help mitigate the adverse effects.
1. Health Risks of Prolonged Sitting
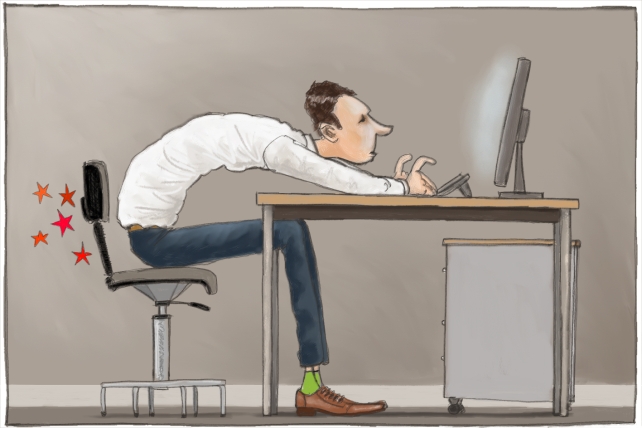
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Sitting for long periods reduces blood circulation, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Obesity and Metabolic Disorders: Physical inactivity leads to slower metabolism, weight gain, and insulin resistance, raising the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Back and Joint Pain: Poor posture and prolonged sitting can cause spinal problems, neck strain, and chronic pain.
Mental Health Issues: Sedentary behavior is linked to higher stress levels, anxiety, and depression.
2. Strategies to Reduce Sitting Time
Take Frequent Breaks: Stand up and stretch every 30-60 minutes.
Use a Standing Desk: Alternating between sitting and standing improves posture and circulation.
Walk More: Incorporate short walks during lunch breaks or phone calls.
Exercise Regularly: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise daily.
Practice Good Posture: Sit straight back, relaxed shoulders, and feet flat on the floor.
Conclusion
Sitting for long hours poses serious health risks, but small changes can make a big difference. Incorporating movement into daily routines, maintaining good posture, and staying active can help counteract the adverse effects of prolonged sitting, leading to a healthier and more active lifestyle.